Aq Tash Fm
Type Locality and Naming
Upper Shyok Valley: Type section is in the volcano-sedimentary succession exposed at the right bank of the Shyok River on way from Saser Brangsa to Chhongtash localites in Upper Shyok valley Eastern Karakoram, India. [Original Publication: Gergan, J. T. & Pant, P. C., 1983. Geology and stratigraphy of eastern Karakoram, Ladakh. In: Thakur, V. C. and Sharma, K. K., (eds), Geology of Indus Suture Zone of Ladakh, Wadia Institute of Himalaya Geology, Dehra Dun, India, 99-106; Juyal, K.P. 2018. Lithostratigraphy, biostratigraphy and palaeogeography of the Eastern Karakoram, India. WIHG Monograph series, No. 3. 1-126.]
Lithology and Thickness
Claystone, Limestone and Volcanics. Comprises of nodular, pink, fragile shale succession at the basal part followed by grey massive limestone commonly containing reworked chert pieces in the limestone resembling microfossils. Nearly 450 m thick succession is traversed by dykes and sills of various dimensions. There are huge eruptions of rhyolite and basic basalt (20–300 m thick) toward the top part of the Aq Tash Formation.
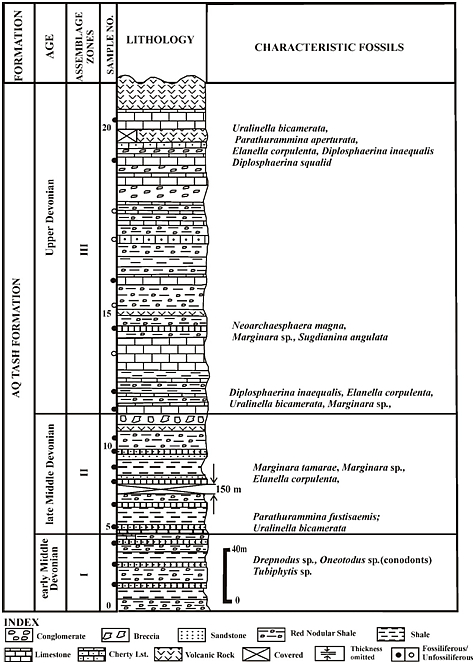
[Figure 1: Biostratigraphic section of Aq Tash Formation (eastern Karakoram) showing the distribution of fauna (after Juyal, 2018)]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Not defined, but next older unit is the Saser Brangsa Fm
Upper contact
Not defined, but next younger unit is the Chhongtash Fm.
Regional extent
Upper Shyok Valley: Not defined.
GeoJSON
Fossils
Foraminifers, conodonts, algae and mollusks shell fragments (Juyal, 2018).
(i) Conodontophorida- Algae Assemblage Zone (Zone-I): Oneotodus sp., Drepanodus sp., indeterminate conodonts, algae, molluscan fauna and ?Ostracods.
(ii) Marginara tamarae – Elanenella corpulanta Assemblage Zone (Zone-II) : Besides zonal fossils this zone has yielded Uranella bicamirata, Parasfegnammina fustisaeformis, ?Uslenia, gastropods and other poorly preserved microfossils.
(iii) Diplosphaerina Inaequalis – Neoarchaesphaera magna Assemblage Zone (Zone-III): Besides zonal fossils this zone yielded Parathurammina operturata, Salpingothurammina, Diplosphaerina magna, ?Sogdiana angulata, ?Arakaevella, Pseudotextularia sp., Tubiphytes sp., (algae) and undetermined gastropod.
Age
Depositional setting
Shallow water environment.
Additional Information